Summary- Gradient Boosting builds an additive model by fitting each new weak learner to the current residual signal.
learning_rate and n_estimators jointly control optimization speed and overfitting risk.- The loss function choice changes robustness to outliers and the shape of the fitted function.
Intuition
#
Gradient Boosting starts with a rough prediction, then repeatedly adds small trees that correct what the current model still gets wrong. Many small, targeted corrections accumulate into a flexible predictor.
Detailed Explanation
#
1
2
3
4
| import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import japanize_matplotlib
from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingRegressor
|
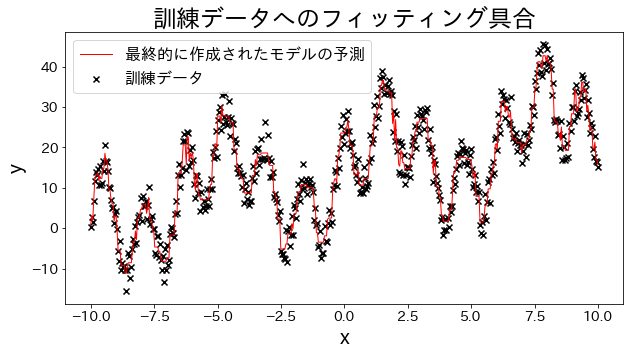
Fit a regression model to training data
#
Create experimental data, waveform data with trigonometric functions added together.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| # training dataset
X = np.linspace(-10, 10, 500)[:, np.newaxis]
noise = np.random.rand(X.shape[0]) * 10
# target
y = (
(np.sin(X).ravel() + np.cos(4 * X).ravel()) * 10
+ 10
+ np.linspace(-10, 10, 500)
+ noise
)
# train gradient boosting
reg = GradientBoostingRegressor(
n_estimators=50,
learning_rate=0.5,
)
reg.fit(X, y)
y_pred = reg.predict(X)
# Check the fitting to the training data
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))
plt.scatter(X, y, c="k", marker="x", label="training data")
plt.plot(X, y_pred, c="r", label="Predictions for the final created model", linewidth=1)
plt.xlabel("x")
plt.ylabel("y")
plt.title("Degree of fitting to training dataset")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
|
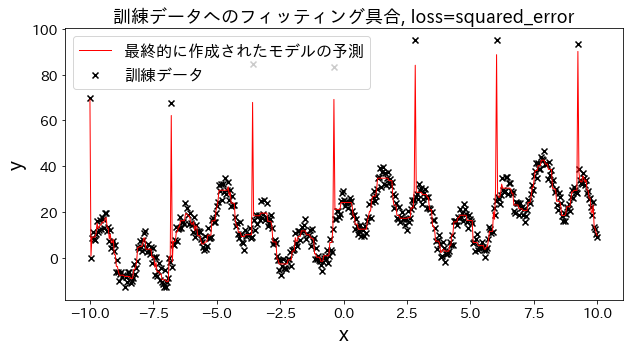
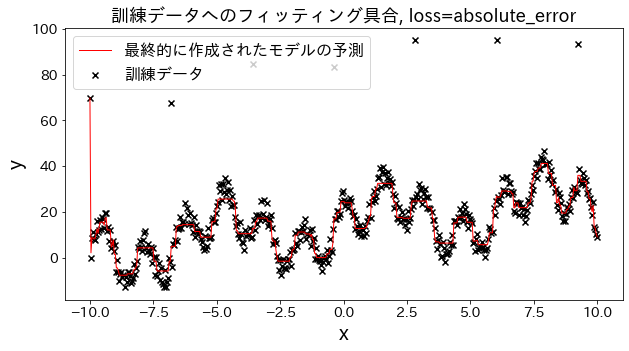
Effect of loss function on results
#
Check how fitting to the training data changes when loss is changed to [“squared_error”, “absolute_error”, “huber”, “quantile”]." It is expected that “absolute_error” and “huber” will not go on to predict outliers since the penalty for outliers is not as large as the squared error.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| # training data
X = np.linspace(-10, 10, 500)[:, np.newaxis]
# prepare outliers
noise = np.random.rand(X.shape[0]) * 10
for i, ni in enumerate(noise):
if i % 80 == 0:
noise[i] = 70 + np.random.randint(-10, 10)
# target
y = (
(np.sin(X).ravel() + np.cos(4 * X).ravel()) * 10
+ 10
+ np.linspace(-10, 10, 500)
+ noise
)
for loss in ["squared_error", "absolute_error", "huber", "quantile"]:
# train gradient boosting
reg = GradientBoostingRegressor(
n_estimators=50,
learning_rate=0.5,
loss=loss,
)
reg.fit(X, y)
y_pred = reg.predict(X)
# Check the fitting to the training data.
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))
plt.scatter(X, y, c="k", marker="x", label="training dataset")
plt.plot(X, y_pred, c="r", label="Predictions for the final created model", linewidth=1)
plt.xlabel("x")
plt.ylabel("y")
plt.title(f"Degree of fitting to training data, loss={loss}", fontsize=18)
plt.legend()
plt.show()
|
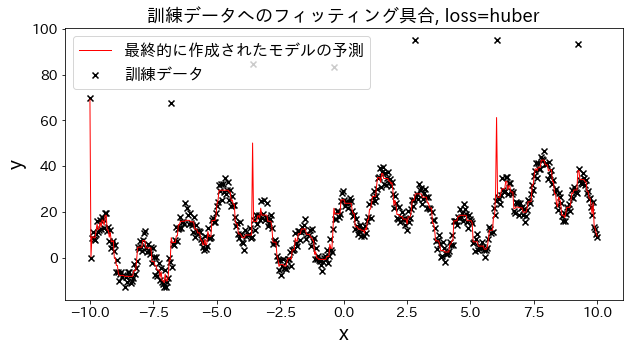
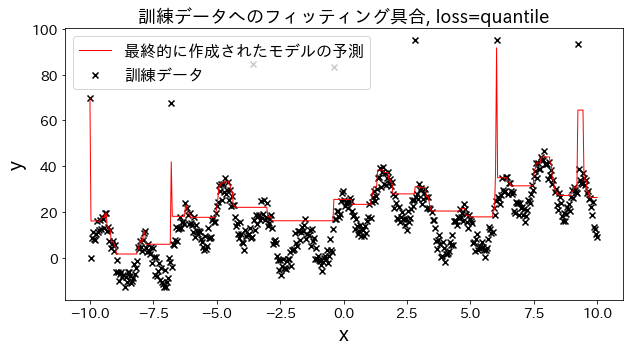
Effect of n_estimators on results
#
You can see how the degree of improvement comes to a head when you increase n_estimators to some extent.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error as MSE
# trainig dataset
X = np.linspace(-10, 10, 500)[:, np.newaxis]
noise = np.random.rand(X.shape[0]) * 10
# target
y = (
(np.sin(X).ravel() + np.cos(4 * X).ravel()) * 10
+ 10
+ np.linspace(-10, 10, 500)
+ noise
)
# Try to create a model with different n_estimators
n_estimators_list = [(i + 1) * 5 for i in range(20)]
mses = []
for n_estimators in n_estimators_list:
reg = GradientBoostingRegressor(
n_estimators=n_estimators,
learning_rate=0.3,
)
reg.fit(X, y)
y_pred = reg.predict(X)
mses.append(MSE(y, y_pred))
# Plotting mean_squared_error for different n_estimators
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))
plt.plot(n_estimators_list, mses, "x")
plt.xlabel("n_estimators")
plt.ylabel("Mean Squared Error(training data)")
plt.grid()
plt.show()
|
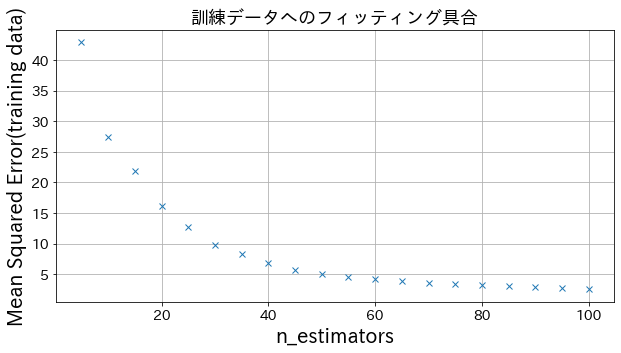
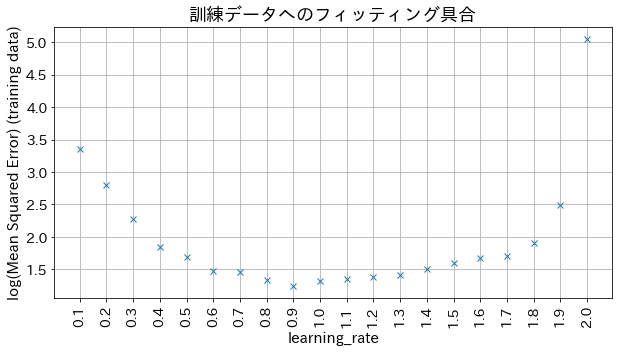
Impact of learning_rate on results
#
If learning_rate is too small, the accuracy does not improve, and if learning_rate is too large, it does not converge.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| # Try to create a model with different n_estimators
learning_rate_list = [np.round(0.1 * (i + 1), 1) for i in range(20)]
mses = []
for learning_rate in learning_rate_list:
reg = GradientBoostingRegressor(
n_estimators=30,
learning_rate=learning_rate,
)
reg.fit(X, y)
y_pred = reg.predict(X)
mses.append(np.log(MSE(y, y_pred)))
# Plotting mean_squared_error for different n_estimators
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))
plt_index = [i for i in range(len(learning_rate_list))]
plt.plot(plt_index, mses, "x")
plt.xticks(plt_index, learning_rate_list, rotation=90)
plt.xlabel("learning_rate", fontsize=15)
plt.ylabel("log(Mean Squared Error) (training data)", fontsize=15)
plt.grid()
plt.show()
|