6.2.8
Check normality with a Q-Q plot
With scipy.stats.probplot you can inspect how closely your data follows a normal distribution. Points that stray far from the reference line indicate stronger departures from normality.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy import stats
data = np.random.normal(loc=0, scale=1, size=500)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(5, 5))
stats.probplot(data, dist="norm", plot=ax)
ax.set_title("Q-Q plot (comparison with the normal distribution)")
ax.grid(alpha=0.2)
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
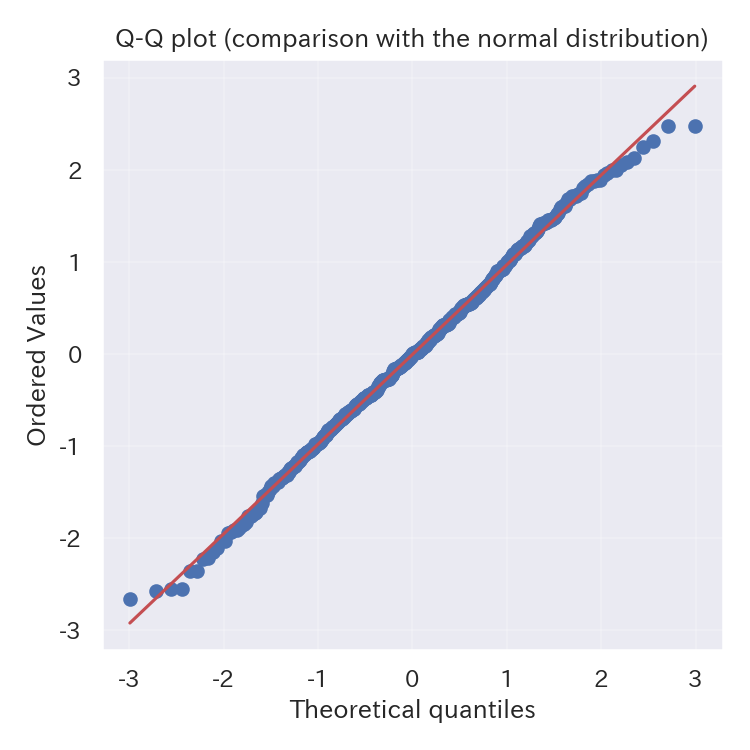
Reading tips #
- If the points lie on the 45° line, the data is close to normal. Curved tails suggest heavy or light tails.
- To test another theoretical distribution, change the
distargument. - Reporting the sample mean and variance alongside the plot helps others interpret the distribution.