6.2.9
Keep points from overlapping with a swarm plot
A swarm plot offsets each observation to avoid overlap, so you can retain individual values while still seeing the overall shape of the distribution.
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
tips = sns.load_dataset("tips")
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6, 4))
sns.swarmplot(data=tips, x="day", y="total_bill", hue="sex", dodge=True, ax=ax)
ax.set_xlabel("Day of week")
ax.set_ylabel("Bill total ($)")
ax.set_title("Bill totals by weekday (swarm plot)")
ax.grid(axis="y", alpha=0.2)
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
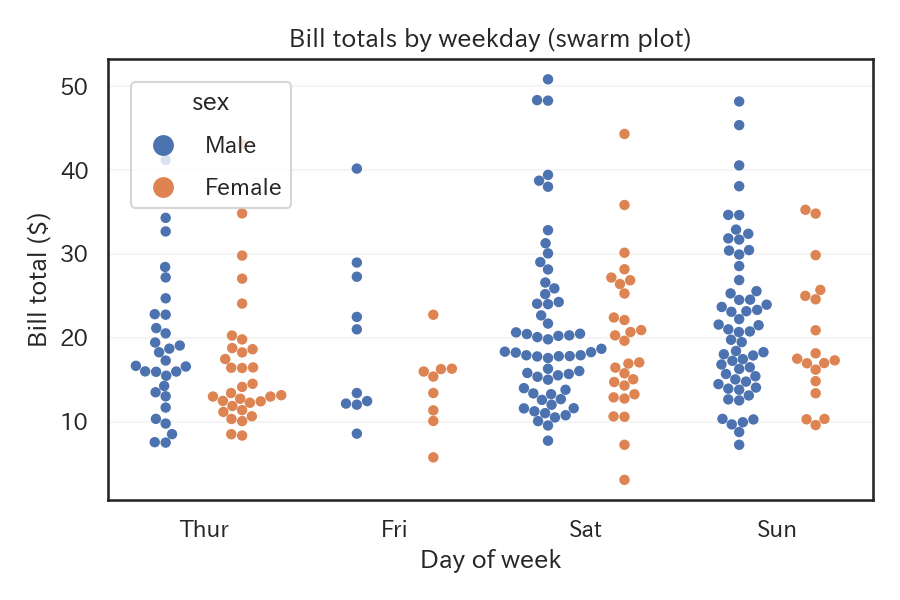
Reading tips #
- The vertical extent of each stack corresponds to local density, and outliers remain visible as individual points.
- With very large data sets, swarm plots become heavy to compute, so sampling or adjusting
sizemay be necessary. - Setting
dodge=Trueseparates each hue category into its own column for easier comparisons.