2.2.4
Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA)
Ringkasan
- LDA mencari arah yang memaksimalkan rasio antara variansi antar kelas dan variansi intra kelas, sehingga berguna untuk klasifikasi sekaligus reduksi dimensi.
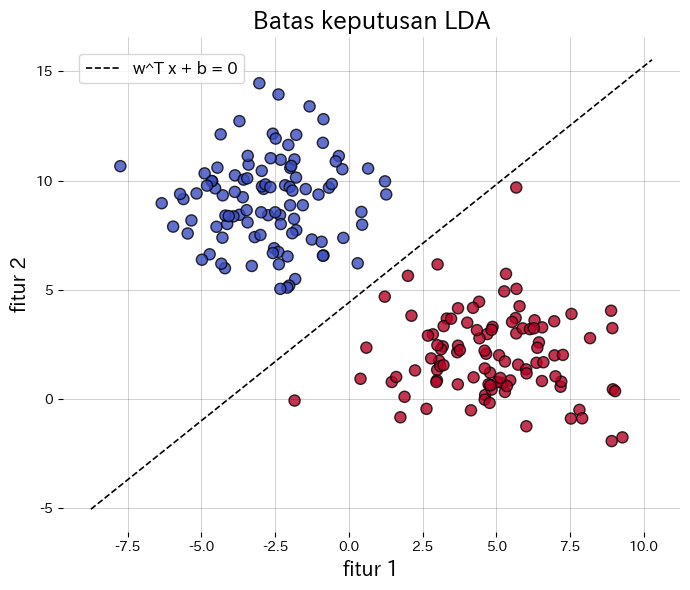
- Batas keputusan berbentuk \(\mathbf{w}^\top \mathbf{x} + b = 0\); di 2D berupa garis dan di 3D berupa bidang, mudah ditafsirkan secara geometris.
- Dengan asumsi tiap kelas berdistribusi Gaussian dan berbagi kovarians yang sama, LDA mendekati klasifikator Bayes optimal.
LinearDiscriminantAnalysisdi scikit-learn memudahkan visualisasi batas keputusan dan inspeksi fitur hasil proyeksi.
Intuisi #
Metode ini dipahami lewat asumsi dasarnya, karakteristik data, dan dampak pengaturan parameter terhadap generalisasi.
Penjelasan Rinci #
Formulasi matematis #
Untuk dua kelas, arah proyeksi \(\mathbf{w}\) memaksimalkan
$$ J(\mathbf{w}) = \frac{\mathbf{w}^\top \mathbf{S}_B \mathbf{w}}{\mathbf{w}^\top \mathbf{S}_W \mathbf{w}}, $$di mana \(\mathbf{S}_B\) adalah matriks sebar antar kelas dan \(\mathbf{S}_W\) adalah matriks sebar intra kelas. Pada kasus multikelas diperoleh hingga \(K-1\) arah proyeksi yang berguna untuk reduksi dimensi.
Eksperimen dengan Python #
Contoh berikut menerapkan LDA pada data sintetis dua kelas, menggambar batas keputusan, dan menampilkan fitur hasil proyeksi 1D. Dengan transform, data hasil proyeksi dapat langsung diperoleh.
from __future__ import annotations
import japanize_matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs
from sklearn.discriminant_analysis import LinearDiscriminantAnalysis
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
def run_lda_demo(
n_samples: int = 200,
random_state: int = 42,
title_boundary: str = "Batas keputusan LDA",
title_projection: str = "Proyeksi satu dimensi oleh LDA",
xlabel: str = "fitur 1",
ylabel: str = "fitur 2",
hist_xlabel: str = "fitur terproyeksi",
class0_label: str = "kelas 0",
class1_label: str = "kelas 1",
) -> dict[str, float]:
"""Train LDA on synthetic blobs and plot boundary plus projection."""
japanize_matplotlib.japanize()
X, y = make_blobs(
n_samples=n_samples,
centers=2,
n_features=2,
cluster_std=2.0,
random_state=random_state,
)
clf = LinearDiscriminantAnalysis(store_covariance=True)
clf.fit(X, y)
accuracy = float(accuracy_score(y, clf.predict(X)))
w = clf.coef_[0]
b = float(clf.intercept_[0])
xs = np.linspace(X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1, 300)
ys_boundary = -(w[0] / w[1]) * xs - b / w[1]
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(7, 6))
ax.set_title(title_boundary)
ax.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, cmap="coolwarm", edgecolor="k", alpha=0.8)
ax.plot(xs, ys_boundary, "k--", lw=1.2, label="w^T x + b = 0")
ax.set_xlabel(xlabel)
ax.set_ylabel(ylabel)
ax.legend(loc="best")
ax.grid(alpha=0.25)
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
X_proj = clf.transform(X)[:, 0]
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 4))
ax.set_title(title_projection)
ax.hist(X_proj[y == 0], bins=20, alpha=0.7, label=class0_label)
ax.hist(X_proj[y == 1], bins=20, alpha=0.7, label=class1_label)
ax.set_xlabel(hist_xlabel)
ax.legend(loc="best")
ax.grid(alpha=0.25)
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
return {"accuracy": accuracy}
metrics = run_lda_demo(
title_boundary="Batas keputusan LDA",
title_projection="Proyeksi satu dimensi oleh LDA",
xlabel="fitur 1",
ylabel="fitur 2",
hist_xlabel="fitur terproyeksi",
class0_label="kelas 0",
class1_label="kelas 1",
)
print(f"Akurasi pelatihan: {metrics['accuracy']:.3f}")
Referensi #
- Fisher, R. A. (1936). The Use of Multiple Measurements in Taxonomic Problems. Annals of Eugenics, 7(2), 179–188.
- Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R., & Friedman, J. (2009). The Elements of Statistical Learning. Springer.