3.3.5
Isolation Forest で異常点を検知する
まとめ- Isolation Forest を使い、教師なしで多次元データの外れ値を検知する。
sklearn.ensemble.IsolationForest の fit/predict で異常スコアとラベルを取得する。- データの分布を仮定せずに外れ値を検出したいときや、高次元データの異常検知に使う。
<p><b>Isolation Forest</b> は木構造を使う教師なし異常検知手法です。ランダムに特徴量と分割点を選びながらデータを分割していき、少ない分割回数で孤立するサンプルを外れ値と判断します。</p>
データの準備
#
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import make_moons
rng = np.random.default_rng(42)
X, _ = make_moons(n_samples=1_000, noise=0.08, random_state=42)
anomaly_index = np.arange(0, 1_000, 60)
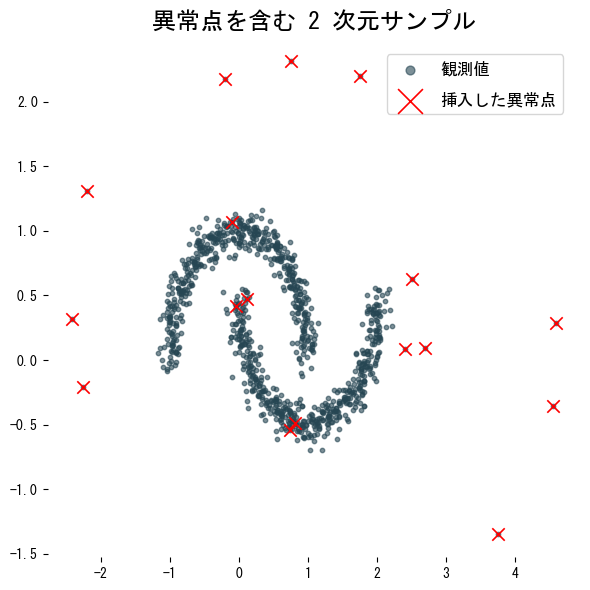
X[anomaly_index] *= 2.5 # 一部サンプルを拡大して外れ点にする
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 6))
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], s=10, alpha=0.6, label="観測値")
plt.scatter(X[anomaly_index, 0], X[anomaly_index, 1], marker="x", s=80, c="red", label="挿入した異常点")
plt.legend()
plt.title("異常点を含む 2 次元サンプル")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
|
Isolation Forest で学習・検知
#
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| from sklearn.ensemble import IsolationForest
detector = IsolationForest(
n_estimators=200,
max_samples=256,
contamination=0.02,
random_state=42,
)
detector.fit(X)
scores = detector.decision_function(X)
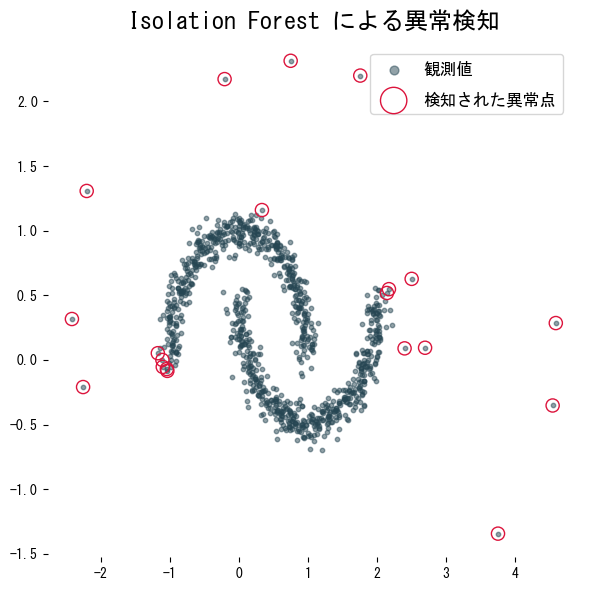
pred = detector.predict(X) # -1: outlier, 1: inlier
detected_index = np.where(pred < 0)[0]
|
contamination はデータ中の異常比率の上限を指定するパラメーターです。比率が不明な場合は小さめの値から調整すると安定します。
結果を可視化する
#
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| plt.figure(figsize=(6, 6))
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], s=10, alpha=0.5, label="観測値")
plt.scatter(
X[detected_index, 0],
X[detected_index, 1],
facecolor="none",
edgecolor="crimson",
s=90,
label="検知された異常点",
)
plt.title("Isolation Forest による異常検知")
plt.legend()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
|
実務でのポイント
#
contamination を大きくしすぎると正常値まで異常判定されやすくなります。監視ログなどでは 0.01 以下から試すのが無難です。max_samples は 256 程度が初期値としてよく使われます。データ量が多い場合は値を増やすと決定境界が滑らかになります。decision_function はスコアを返すため、後からしきい値を変更したい場合に便利です。predict は -1/1 のラベルを直接返します。- 特徴量ごとにスケールが大きく異なる場合は StandardScaler や RobustScaler と組み合わせておくと検知性能が安定します。

