2.9.1
การตรวจจับความผิดปกติ ①
- สรุปเป้าหมาย สมมติฐาน และเงื่อนไขที่เหมาะสมของวิธีนี้.
- ตรวจสอบว่ากฎการอัปเดตหรือเกณฑ์การแบ่งส่งผลต่อพฤติกรรมโมเดลอย่างไร.
- ใช้ตัวอย่างโค้ดเพื่อกำหนดแนวทางปรับพารามิเตอร์อย่างเป็นรูปธรรม.
สัญชาตญาณ #
การตรวจจับความผิดปกติ ① ควรเข้าใจผ่านสมมติฐาน กลไกการปรับปรุงโมเดล และรูปแบบความผิดพลาดบนข้อมูลจริง เพื่อให้เลือกโมเดลและปรับพารามิเตอร์ได้อย่างเหมาะสม.
คำอธิบายโดยละเอียด #
1. เตรียมข้อมูลทดลอง #
ในตัวอย่างนี้ใช้ข้อมูลจาก Numenta Anomaly Benchmark (NAB)
และทดลองด้วย ADTK (Anomaly Detection Toolkit)
import pandas as pd
from adtk.data import validate_series
s_train = pd.read_csv(
"./training.csv", index_col="timestamp", parse_dates=True, squeeze=True
)
s_train = validate_series(s_train)
print(s_train.head())
from adtk.visualization import plot
plot(s_train)
2. วิธีตรวจจับที่ใช้บ่อย #
ADTK มีตัวตรวจจับหลายแบบ ที่นี่เลือก 5 วิธีหลักมาเปรียบเทียบ
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from adtk.detector import (
AutoregressionAD,
InterQuartileRangeAD,
LevelShiftAD,
PersistAD,
SeasonalAD,
)
model_dict = {
"LevelShiftAD": LevelShiftAD(window=5),
"SeasonalAD": SeasonalAD(),
"PersistAD": PersistAD(c=3.0, side="positive"),
"InterQuartileRangeAD": InterQuartileRangeAD(c=1.5),
"AutoregressionAD": AutoregressionAD(n_steps=14, step_size=24, c=3.0),
}
for model_name, model in model_dict.items():
anomalies = model.fit_detect(s_train)
plot(s_train, anomaly=anomalies, anomaly_color="red", anomaly_tag="marker")
plt.title(model_name)
plt.show()
3. แนวคิดและสมการของแต่ละวิธี #
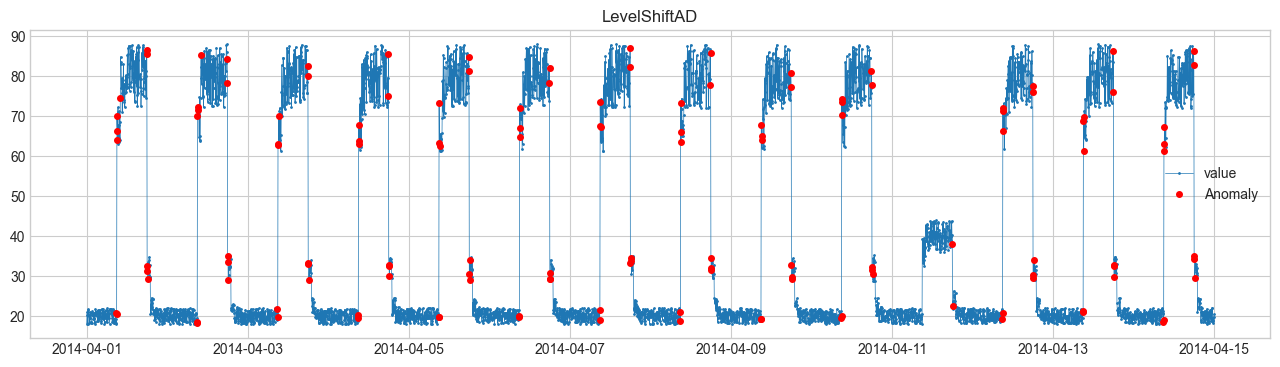
(1) LevelShiftAD (การเปลี่ยนระดับ) #
ตรวจว่าค่าเฉลี่ยเปลี่ยนฉับพลันหรือไม่
เช่น ค่าเซนเซอร์กระโดดขึ้นหรือลงแบบทันที
ถ้า \(|\Delta_t|\) ใหญ่พอ → ถือเป็นความผิดปกติ
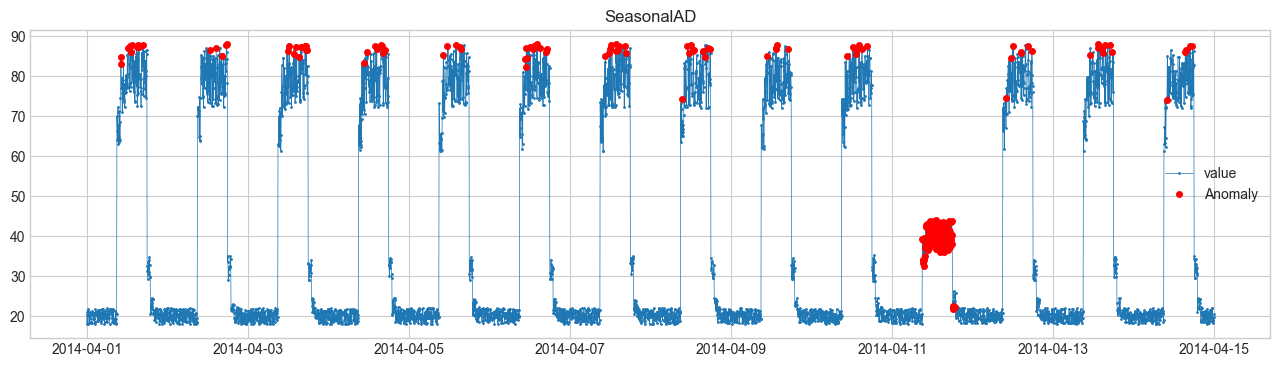
(2) SeasonalAD (เบี่ยงจากฤดูกาล) #
เรียนรู้รูปแบบตามคาบ แล้วตรวจจุดที่เบี่ยงจากรูปแบบนั้น
เช่น จำนวนผู้ใช้งานรายวันที่พุ่งสูงผิดปกติ
ถ้า \(e_t\) ใหญ่ → ผิดปกติ
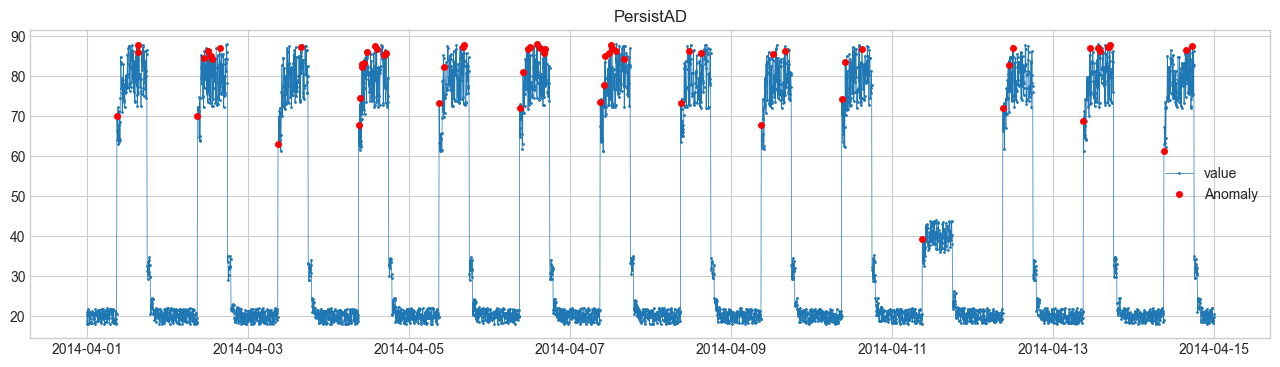
(3) PersistAD (ค่าคงค้างผิดปกติ) #
ดูว่าแตกต่างจากค่าก่อนหน้ามากเกินไปหรือไม่
$$ |x_t - x_{t-1}| > c \cdot \sigma $$ถ้าเกิน \(c\) → ผิดปกติ
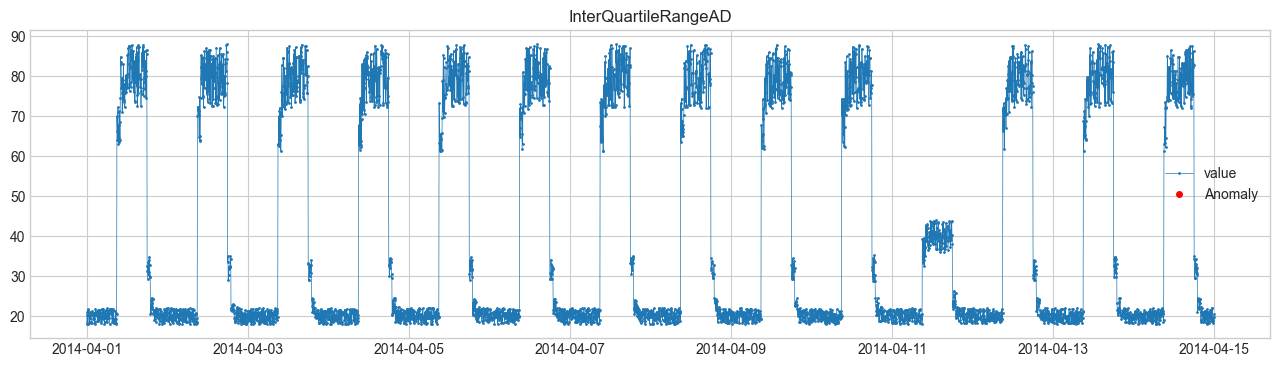
(4) InterQuartileRangeAD (ช่วงควอไทล์) #
ตรวจ outlier ด้วยสถิติ
ใช้ควอไทล์ที่ 1 \(Q1\), ควอไทล์ที่ 3 \(Q3\) และช่วงควอไทล์ \(IQR=Q3-Q1\)
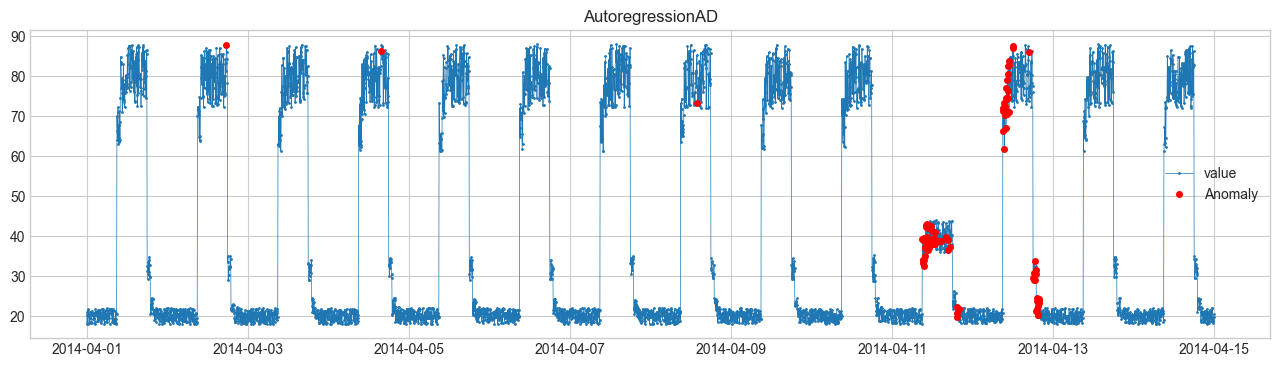
(5) AutoregressionAD (ออโตเรเกรสชัน) #
พยากรณ์อนาคตจากอดีต แล้วดูค่าคลาดเคลื่อน
$$ x_t \approx \sum_{i=1}^p \phi_i x_{t-i} + \epsilon_t $$ถ้าเศษเหลือ \(\epsilon_t\) ใหญ่ → ผิดปกติ
4. ผลการแสดงผล #