2.4.2
Stacking
สรุป
- สรุปเป้าหมาย สมมติฐาน และเงื่อนไขที่เหมาะสมของวิธีนี้.
- ตรวจสอบว่ากฎการอัปเดตหรือเกณฑ์การแบ่งส่งผลต่อพฤติกรรมโมเดลอย่างไร.
- ใช้ตัวอย่างโค้ดเพื่อกำหนดแนวทางปรับพารามิเตอร์อย่างเป็นรูปธรรม.
สัญชาตญาณ #
Stacking คือแนวคิดที่สร้างหลายโมเดล แล้วนำผลลัพธ์ของโมเดลเหล่านั้นไปเป็นอินพุตให้โมเดลอีกตัวหนึ่ง ในหน้านี้เราจะทดลอง stacking และดูว่าโมเดลใดในชั้นแรกมีผลต่อการทำนายมากที่สุด
คำอธิบายโดยละเอียด #
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.ensemble import StackingClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score
from sklearn.tree import export_graphviz
from subprocess import call
สร้างข้อมูลสำหรับการทดลอง #
# Create data with 20 features
n_features = 20
X, y = make_classification(
n_samples=2500,
n_features=n_features,
n_informative=10,
n_classes=2,
n_redundant=0,
n_clusters_per_class=4,
random_state=777,
)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.33, random_state=777
)
พล็อตข้อมูลหลายมุมมอง #
ยืนยันว่าข้อมูลไม่สามารถแบ่งด้วยกฎง่าย ๆ ได้ชัดเจน
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.subplot(2, 2, 1)
plt.scatter(X[:, 2], X[:, 7], c=y)
plt.xlabel("x2")
plt.ylabel("x7")
plt.subplot(2, 2, 2)
plt.scatter(X[:, 4], X[:, 9], c=y)
plt.xlabel("x4")
plt.ylabel("x9")
plt.subplot(2, 2, 3)
plt.scatter(X[:, 5], X[:, 1], c=y)
plt.xlabel("x5")
plt.ylabel("x1")
plt.subplot(2, 2, 4)
plt.scatter(X[:, 1], X[:, 3], c=y)
plt.xlabel("x1")
plt.ylabel("x3")
plt.show()
เปรียบเทียบ Stacking กับ Random Forest #
การจำแนกด้วย Random Forest #
model = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=50, max_depth=5, random_state=777)
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
rf_score = roc_auc_score(y_test, y_pred)
print(f"ROC-AUC = {rf_score}")
ROC-AUC = 0.855797033310609
Stacking ด้วยหลายต้นไม้ #
ยืนยันว่า stacking ที่ใช้เฉพาะ DecisionTreeClassifier ยังไม่ช่วยให้ดีขึ้นมากนัก
# Models used in base learner
estimators = [
("dt1", DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=3, random_state=777)),
("dt2", DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=4, random_state=777)),
("dt3", DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=5, random_state=777)),
("dt4", DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=6, random_state=777)),
]
# Number of models included in base learner
n_estimators = len(estimators)
# aggregation model
final_estimator = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=3, random_state=777)
# train base-learner and aggregation model
clf = StackingClassifier(estimators=estimators, final_estimator=final_estimator)
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
# evaluate
y_pred = clf.predict(X_test)
clf_score = roc_auc_score(y_test, y_pred)
print("ROC-AUC")
print(f"Decision Tree Stacking={clf_score}, Random Forest={rf_score}")
ROC-AUC
Decision Tree Stacking=0.7359716965608031, Random Forest=0.855797033310609
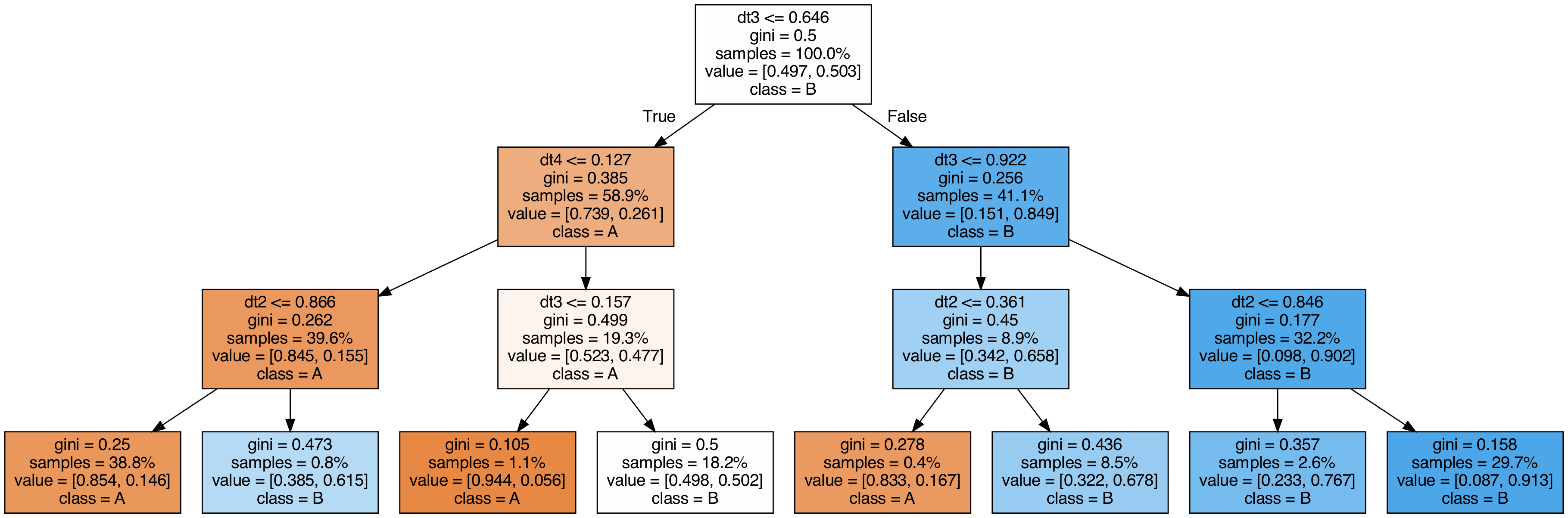
แสดงต้นไม้ที่ใช้ใน stacking #
export_graphviz(
clf.final_estimator_,
out_file="tree_final_estimator.dot",
class_names=["A", "B"],
feature_names=[e[0] for e in estimators],
proportion=True,
filled=True,
)
call(
[
"dot",
"-Tpng",
"tree_final_estimator.dot",
"-o",
f"tree_final_estimator.png",
"-Gdpi=200",
]
)
display(Image(filename="tree_final_estimator.png"))
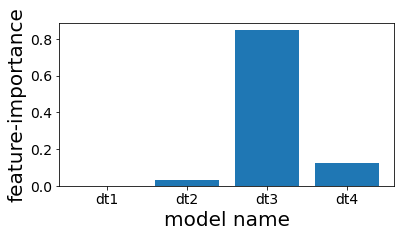
ดู feature importance ของต้นไม้ในชั้นบน #
จะเห็นว่าถึงจะ stacking หลายต้น แต่ท้ายที่สุดต้นไม้ตัวที่ 4 ถูกใช้แทบทั้งหมด
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 3))
plot_index = [i for i in range(n_estimators)]
plt.bar(plot_index, clf.final_estimator_.feature_importances_)
plt.xticks(plot_index, [e[0] for e in estimators])
plt.xlabel("model name")
plt.ylabel("feature-importance")
plt.show()
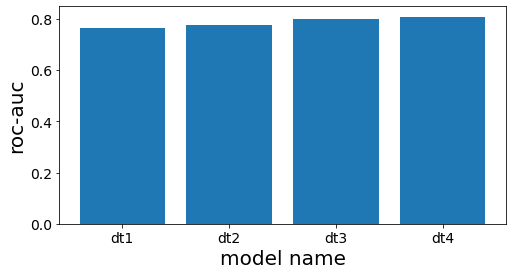
ตรวจสอบประสิทธิภาพของแต่ละต้นไม้ใน base learner #
scores = []
for clf_estim in clf.estimators_:
print("====")
y_pred = clf_estim.predict(X_test)
scr = roc_auc_score(y_test, y_pred)
scores.append(scr)
print(clf_estim)
print(scr)
n_estimators = len(estimators)
plot_index = [i for i in range(n_estimators)]
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 4))
plt.bar(plot_index, scores)
plt.xticks(plot_index, [e[0] for e in estimators])
plt.xlabel("model name")
plt.ylabel("roc-auc")
plt.show()
====
DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=3, random_state=777)
0.7660117774277722
====
DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=4, random_state=777)
0.7744128916993818
====
DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=5, random_state=777)
0.8000158677919086
====
DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=6, random_state=777)
0.8084639977432473