2.3.1
Decision Tree (Classifier)
- Decision tree classifier แบ่งพื้นที่ฟีเจอร์ด้วยคำถามแบบ if-then จนถึงใบไม้ที่มีคลาสเด่นชัด
- ใช้เกณฑ์อย่าง Gini หรือ entropy เพื่อวัดคุณภาพของการแบ่ง
- ปรับความลึกและขนาดใบเพื่อลด overfitting แต่ยังคงความสามารถในการอธิบายผล
- การวาดขอบเขตการตัดสินใจและโครงสร้างต้นไม้ช่วยสื่อสารกับผู้เกี่ยวข้องได้ง่าย
สัญชาตญาณ #
การเข้าใจวิธีนี้ควรดูสมมติฐานของโมเดล ลักษณะข้อมูล และผลของการตั้งค่าพารามิเตอร์ต่อการทั่วไปของโมเดล
คำอธิบายโดยละเอียด #
1. ภาพรวม #
ต้นไม้ตัดสินใจเป็นโมเดลที่แบ่งพื้นที่อินพุตแบบวนซ้ำ โดยโหนดแต่ละจุดถามคำถามเช่น “(x_j \le s) หรือไม่?” สำหรับงานจำแนก เราต้องการให้ใบไม้มีความบริสุทธิ์สูง เพื่อให้ผลทำนายมีความชัดเจน โมเดลจึงทำหน้าที่เหมือนชุดกฎที่ตรวจสอบได้ง่าย
2. ตัวชี้วัดความไม่บริสุทธิ์ #
ให้ (t) เป็นโหนด และ (p_k) เป็นสัดส่วนของคลาส (k) ภายในโหนดนั้น
$$ \mathrm{Gini}(t) = 1 - \sum_k p_k^2, $$$$ H(t) = - \sum_k p_k \log p_k. $$ถ้าแบ่งโหนด (t) ด้วยฟีเจอร์ (x_j) และค่า (s) จะได้การลดความไม่บริสุทธิ์เป็น
$$ \Delta I = I(t) - \frac{n_L}{n_t} I(t_L) - \frac{n_R}{n_t} I(t_R), $$โดย (I(\cdot)) คือ Gini หรือ entropy, (t_L), (t_R) คือโหนดย่อย และ (n_t) คือจำนวนตัวอย่าง ระบบจะเลือก split ที่ทำให้ (\Delta I) สูงสุด
3. ตัวอย่าง Python #
โค้ดด้านล่างสร้างข้อมูลสองคลาสด้วย make_classification แล้วฝึก DecisionTreeClassifier
จากนั้นวาดขอบเขตการตัดสินใจ โดยเปลี่ยน criterion เป็น "entropy" จะสลับไปใช้ entropy
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier, plot_tree
n_classes = 2
X, y = make_classification(
n_samples=100,
n_features=2,
n_redundant=0,
n_informative=2,
random_state=2,
n_classes=n_classes,
n_clusters_per_class=1,
)
clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion="gini", random_state=0).fit(X, y)
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1
y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() + 1
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(
np.arange(x_min, x_max, 0.1),
np.arange(y_min, y_max, 0.1),
)
Z = clf.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()]).reshape(xx.shape)
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, cmap=plt.cm.Pastel1, alpha=0.6)
plt.xlabel("x1")
plt.ylabel("x2")
for i, color, label_name in zip(range(n_classes), ["r", "b"], ["A", "B"]):
idx = np.where(y == i)
plt.scatter(X[idx, 0], X[idx, 1], c=color, label=label_name, edgecolor="k")
plt.legend()
plt.title("Decision regions created by a tree")
plt.show()
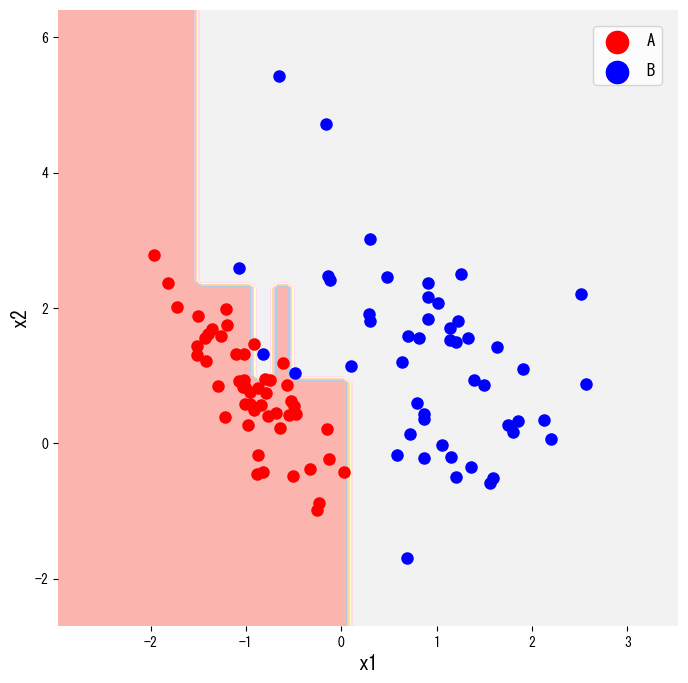
ต้นไม้ยังสามารถวาดเป็นแผนภาพด้วย plot_tree เพื่อใช้ในรายงานได้
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 12))
plot_tree(clf, filled=True, feature_names=["x1", "x2"], class_names=["A", "B"])
plt.show()

4. อ้างอิง #
- Breiman, L., Friedman, J. H., Olshen, R. A., & Stone, C. J. (1984). Classification and Regression Trees. Wadsworth.
- scikit-learn developers. (2024). Decision Trees. https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/tree.html